In the realm of pain management, hydrocodone and oxycodone stand as two of the most commonly prescribed opioids, each with its unique properties and potential risks. For individuals navigating the challenging waters of addiction, understanding the differences between these two medications is crucial. As potent narcotics, both hydrocodone and oxycodone carry significant risks of dependency and abuse, making professional guidance essential for anyone struggling with substance use disorder.
At Westwind Recovery®, we are dedicated to unraveling the complexities of these powerful drugs, offering compassionate support, and providing comprehensive treatment options tailored to foster recovery and empower individuals on their journey to wellness. We will explore the similarities and differences between hydrocodone and oxycodone, including their chemical structures, medical uses, side effects, risk of addiction, and withdrawal symptoms.
Understanding Hydrocodone and Oxycodone
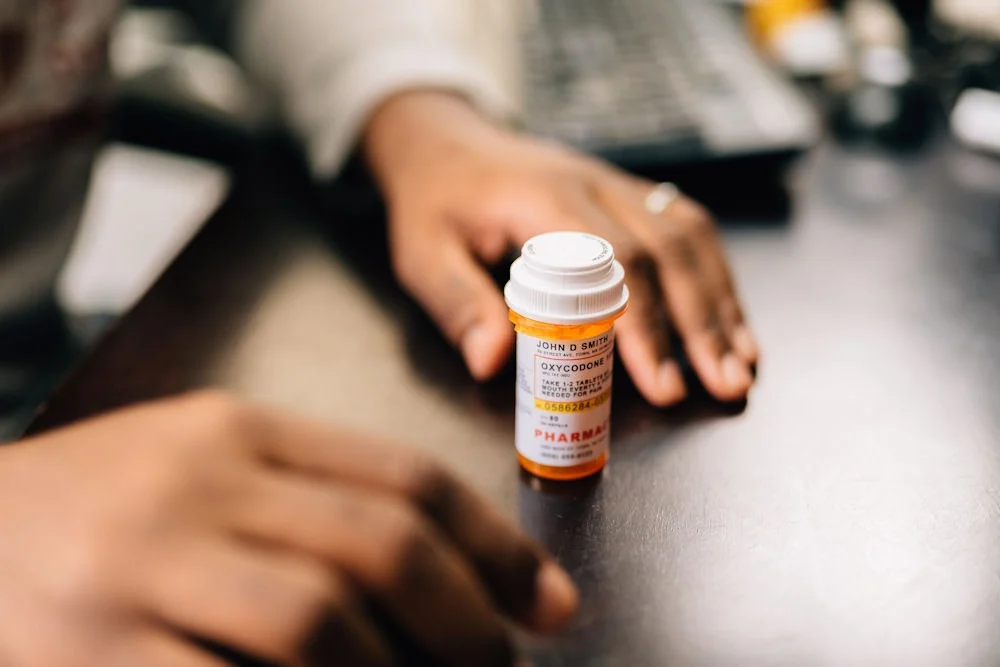
Before diving into the specific details, let’s first gain a basic understanding of hydrocodone and oxycodone separately.
Hydrocodone and oxycodone are both powerful opioid medications commonly prescribed to manage pain. These drugs belong to the same class of medications and work by binding to specific receptors in the brain and spinal cord, effectively reducing the perception of pain. While they are similar in many ways, there are also key differences between the two drugs that are important to consider.
Hydrocodone is a semi-synthetic opioid medication used primarily to relieve moderate to severe pain. It acts on the central nervous system to alleviate pain and is classified as a Schedule II drug due to its potential for abuse and dependency. It’s often combined with other pain relievers like acetaminophen in medications such as Vicodin.
Hydrocodone is known for its effectiveness in providing pain relief. However, due to its opioid nature, hydrocodone also carries a risk of tolerance, dependence, and potential misuse if not taken as directed by a healthcare provider.
Oxycodone, on the other hand, is a pure opioid agonist derived from thebaine, another alkaloid found in opium poppy. It is available in both immediate-release and extended-release formulations and is often prescribed for moderate to severe pain that requires continuous, around-the-clock relief.
Similar to hydrocodone, oxycodone is effective in managing pain but also comes with potential side effects and risks. It is crucial for individuals taking oxycodone to be aware of the potential for respiratory depression, constipation, and addiction. Healthcare providers typically closely monitor patients on oxycodone to ensure its safe and appropriate use.
Hydrocodone and oxycodone are both strong painkillers often prescribed for managing pain. Hydrocodone is usually mixed with other pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to boost its effectiveness, while oxycodone is often given on its own for more severe pain. In the body, hydrocodone is broken down in the liver into a stronger form, which contributes to its pain-relieving abilities. Oxycodone is also processed in the liver, turning into other substances that help with pain but can also cause side effects and interact with other medications. Understanding how these drugs work is important for doctors to ensure they provide the best pain relief while reducing the risk of side effects.
The Medical Uses of Hydrocodone and Oxycodone
Hydrocodone and oxycodone are commonly prescribed in various medical settings for pain management. Let’s explore their specific applications.
Both hydrocodone and oxycodone belong to a class of medications known as opioids, which are powerful pain relievers derived from the opium poppy plant. These medications work by binding to specific receptors in the brain and spinal cord, effectively blocking pain signals and providing relief to patients suffering from various types of pain.
Hydrocodone in Pain Management
Hydrocodone is used in pain management primarily to treat moderate to severe pain. It’s often prescribed when other pain relievers, like non-opioid medications, which are not effective. Hydrocodone is typically combined with other pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen to enhance its effectiveness.
Common conditions for which hydrocodone might be prescribed include:
- Post-surgical pain: To manage pain following surgery.
- Injury-related pain: Such as pain from fractures or severe sprains.
- Chronic pain conditions: Including conditions like arthritis or back pain when other treatments have not been successful.
- Cancer-related pain: To help manage pain associated with cancer or cancer treatments.
It’s important for hydrocodone to be used under strict medical supervision due to its potential for addiction and side effects.
Oxycodone in Pain Management
Oxycodone is used in pain management to treat moderate to severe pain, especially when around-the-clock relief is needed. It’s often prescribed when other pain medications are insufficient. Oxycodone can be used on its own or in combination with other pain relievers.
Common conditions for which oxycodone might be prescribed include:
- Post-operative pain: To manage pain after surgery.
- Severe injury pain: Such as from major fractures or trauma.
- Chronic pain conditions: Including severe arthritis, back pain, or neuropathic pain.
- Cancer-related pain: To help manage significant pain associated with cancer or its treatments.
Similar to hydrocodone, oxycodone can also be habit-forming if not taken as directed. Patients should be closely monitored by their healthcare providers while using oxycodone to ensure its safe and effective use in managing their pain.
The Side Effects of Hydrocodone and Oxycodone
Like any medication, hydrocodone and oxycodone carry the risk of side effects. It is important to be aware of these potential adverse effects that may arise during treatment. Hydrocodone and oxycodone are both powerful opioid medications commonly prescribed to manage moderate to severe pain. While these medications can be highly effective in providing relief, they also come with a range of side effects that patients should be mindful of.
Common Side Effects of Hydrocodone
When taking hydrocodone, patients may experience common side effects such as constipation, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. These side effects are usually temporary and tend to diminish over time.
In addition to the common side effects, some patients may also experience less common but more serious side effects from hydrocodone, such as respiratory depression, allergic reactions, and mood changes. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these severe side effects occur.
Common Side Effects of Oxycodone
Oxycodone can also cause a range of common side effects, including constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, and headache. Just as with hydrocodone, these side effects typically fade as the body adjusts to the medication.
Similar to hydrocodone, oxycodone can also lead to more serious side effects like respiratory depression, especially when taken in high doses or combination with other central nervous system depressants. Patients should be cautious when using oxycodone and follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
The Risk of Addiction: Hydrocodone and Oxycodone
 One of the most significant concerns associated with opioid medications is the risk of addiction. Both hydrocodone and oxycodone have the potential to lead to physical and psychological dependence if not used as prescribed.
One of the most significant concerns associated with opioid medications is the risk of addiction. Both hydrocodone and oxycodone have the potential to lead to physical and psychological dependence if not used as prescribed.
It is essential to understand that addiction to hydrocodone and oxycodone is a complex issue that can affect individuals from all walks of life. Factors such as genetic predisposition, mental health conditions, and environmental influences can contribute to the development of addiction. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to conduct thorough assessments and provide personalized treatment plans to address the specific needs of each patient.
Understanding Hydrocodone Addiction
Hydrocodone, like other opioids, can create dependency when used for prolonged periods or in higher doses than prescribed. It is crucial for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and be aware of the signs of addiction, such as craving the medication, increased tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
Furthermore, education plays a vital role in preventing hydrocodone addiction. Patients should be informed about the potential risks associated with long-term opioid use and the importance of using alternative pain management strategies whenever possible. By promoting awareness and providing resources for addiction prevention, healthcare providers can empower patients to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Understanding Oxycodone Addiction
Oxycodone carries a similar risk of addiction to hydrocodone. Patients should use it only as directed and communicate openly with their healthcare provider to minimize the chances of developing an addiction. Recognizing the signs of dependency, such as compulsive drug-seeking behavior or escalating dosages, is vital for intervention and seeking proper medical help.
In addition to individual efforts to prevent oxycodone addiction, community-based initiatives, and public health campaigns play a crucial role in raising awareness about the dangers of opioid misuse. By fostering collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations, it is possible to implement comprehensive strategies that address the root causes of addiction and promote access to evidence-based treatment options.
Withdrawal and Detoxification from Hydrocodone and Oxycodone
When discontinuing hydrocodone or oxycodone, patients may experience withdrawal symptoms as their bodies adjust to the absence of the opioid medication. Withdrawal should be conducted under medical supervision to ensure a safe and successful detox process.
It is crucial for individuals undergoing withdrawal from hydrocodone or oxycodone to have a supportive environment during this challenging time. Family members, friends, or support groups can play a significant role in providing emotional support and encouragement throughout the detox process. Additionally, counseling and therapy sessions can help individuals address the underlying issues that may have led to opioid dependence, paving the way for long-term recovery.
Hydrocodone Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms from hydrocodone can include restlessness, anxiety, muscle aches, insomnia, diarrhea, and flu-like symptoms. Gradual tapering and appropriate medical support are essential for managing withdrawal effectively.
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend alternative therapies or non-opioid pain management strategies to help individuals cope with pain without relying on hydrocodone. These approaches can include physical therapy, acupuncture, mindfulness techniques, or over-the-counter pain relievers. By exploring diverse pain management options, patients can reduce their dependence on opioids and improve their overall well-being.
Oxycodone Withdrawal Symptoms
Similarly, oxycodone withdrawal may present symptoms such as agitation, sweating, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and cravings. Medical professionals can devise personalized tapering schedules and provide appropriate medications to alleviate withdrawal symptoms and ensure a smoother detoxification process.
It is essential for individuals undergoing oxycodone withdrawal to stay hydrated and maintain a nutritious diet to support their bodies during this challenging period. Adequate hydration and nourishment can help alleviate some withdrawal symptoms and promote overall health and recovery. Engaging in light physical activities, such as gentle exercises or walks, can also aid in improving mood and reducing discomfort during the detoxification process.
Do You Have More Questions on Substance Abuse?
Both hydrocodone and oxycodone are widely used opioid medications with similarities and differences in terms of chemical structures, medical uses, side effects, risk of addiction, and withdrawal symptoms. Understanding these distinctions can help patients and healthcare providers choose the most appropriate pain management option while minimizing potential risks.
Do you have more questions related to substance abuse? Contact our professionals at Westwind Recovery®! We can help you navigate the complex issues surrounding substance abuse and addiction. Our outpatient drug rehab in Los Angeles programs provide compassionate care and personalized treatment options to support lasting recovery.

Dr. Deena is the Chief Clinical Officer of Westwind Recovery®, an award-winning outpatient treatment center in Los Angeles where she oversees the clinical and administrative program and treatment methods. Dr. Deena is a doctor of psychology and licensed clinical social worker since 1993. LCSW #20628. Originally from the East Coast, Dr. Deena has worked running treatment centers, worked as a therapist in psychiatric hospitals as well as school settings and currently has a thriving private practice in the LA area. Dr. Deena has appeared regularly on the Dr. Phil Show as an expert since 2003. She has also been featured on many other TV shows, podcasts and has contributed to written publications as well as podcasts.