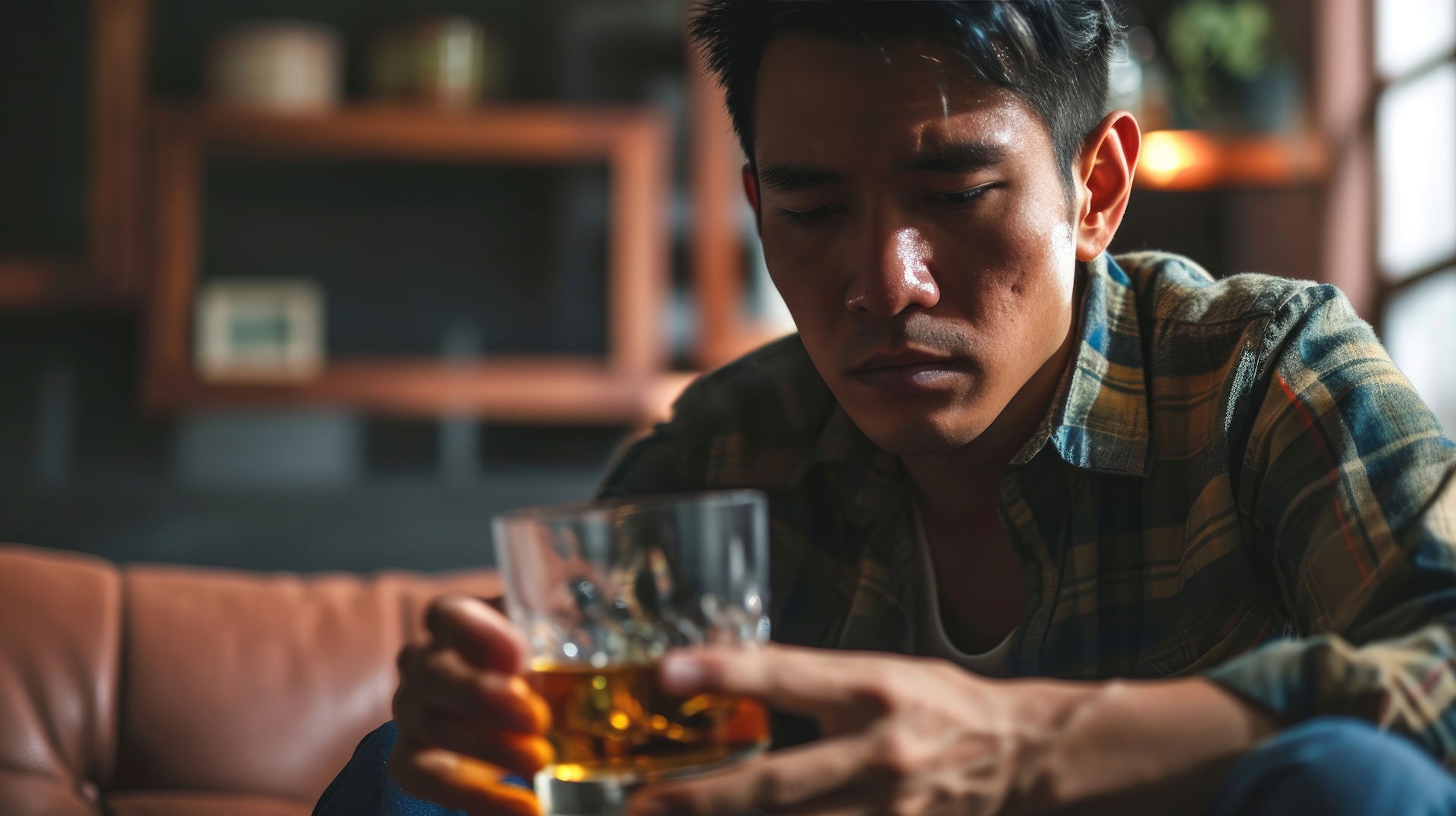
The answer to this question is yes. While not everyone who goes through alcohol withdrawal will experience life-threatening symptoms, it can be fatal in certain cases. The risk of death from alcohol withdrawal is highest for individuals who have been heavy drinkers for a long time and suddenly stop drinking. It is estimated that 3-5% of people who experience alcohol withdrawal will develop DTs, and about 4% of those individuals will die from them.
What is Alcohol Withdrawal?
Alcohol withdrawal is a set of symptoms that occur when someone dependent on alcohol suddenly stops or reduces their alcohol consumption. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can start as soon as 6 hours after the last drink.
The severity and duration of alcohol withdrawal can vary depending on several factors, including the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption, overall health, and previous experiences with withdrawal.
How is Alcohol Withdrawal Diagnosed?
Alcohol withdrawal is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and an evaluation of the individual’s medical history and alcohol use. A healthcare professional may also conduct blood tests to measure the level of alcohol in the body and rule out other potential causes for symptoms. It is important to be honest and open with your healthcare provider about your alcohol consumption to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Understanding Alcohol Withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal occurs when someone who has been drinking heavily for a prolonged period suddenly stops or significantly reduces their alcohol intake. This sudden decrease in alcohol consumption causes the body to go into shock as it tries to adjust to functioning without alcohol. It is important to note that alcohol withdrawal is not the same as a hangover, which is typically experienced after a night of heavy drinking.
During alcohol withdrawal, the body experiences a range of physical and psychological symptoms. These can include:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Anxiety and irritability
In more severe cases, individuals may also experience hallucinations and seizures. These symptoms usually appear within 6-24 hours after the last drink and can continue for several days.
Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal
The severity and type of symptoms experienced during alcohol withdrawal vary depending on the individual’s level of dependence, how much and how often they drink, and other factors such as age and overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Sweating
- Rapid heart rate
- Shaking or tremors
In severe cases, alcohol withdrawal can lead to delirium tremens (DTs), which includes symptoms such as confusion, hallucinations, and seizures. DTs are considered a medical emergency and require immediate treatment.
What are Delirium Tremens?
Delirium tremens, also known as “the DTs,” is a severe form of alcohol withdrawal that can be life-threatening. It typically occurs within 48-96 hours after an individual has stopped drinking and is characterized by sudden and severe changes in the brain and nervous system. Symptoms of DTs include confusion, agitation, hallucinations, fever, seizures, and changes in heart rate and blood pressure. DTs can lead to cardiovascular collapse, respiratory failure, and other serious complications.
However, it’s important to note that not everyone who experiences alcohol withdrawal will develop DTs. Most people will only experience mild to moderate symptoms such as nausea, insomnia, anxiety, and headaches. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and make it difficult to function, but they are not usually life-threatening.
The Dangers of Alcohol Withdrawal
While not everyone will experience dangerous or life-threatening symptoms during alcohol withdrawal, it is important to understand the potential risks. DTs are the most severe form of alcohol withdrawal and can occur 2-3 days after the last drink. Individuals experiencing DTs may have a rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and fever. They may also experience hallucinations, confusion, and disorientation.
Without proper medical treatment, DTs can lead to respiratory failure, seizures, and death. This is why it is crucial for individuals who are at risk of developing DTs to seek medical help during alcohol withdrawal.
It is also important to mention that alcohol withdrawal can exacerbate underlying health conditions. For example, if someone has a pre-existing heart condition, the stress of alcohol withdrawal could potentially trigger a heart attack or other serious complications. This is why individuals need to seek medical supervision during alcohol withdrawal, especially if they have any underlying health issues.
Avoiding Alcohol Withdrawal
 The best way to avoid experiencing potentially life-threatening alcohol withdrawal is to seek help before it becomes a problem. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol addiction, there are resources available to help. It is essential to address the issue before it leads to dangerous withdrawal symptoms and potential death.
The best way to avoid experiencing potentially life-threatening alcohol withdrawal is to seek help before it becomes a problem. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol addiction, there are resources available to help. It is essential to address the issue before it leads to dangerous withdrawal symptoms and potential death.
Some ways to prevent alcohol withdrawal include:
- Seeking treatment for alcohol addiction
- Gradually reducing alcohol consumption instead of quitting cold turkey
- Talking to a healthcare professional about safe detox methods
- Having a support system in place during the detox process
How to Manage Alcohol Withdrawal
For those who are experiencing alcohol withdrawal, there are ways to manage and minimize the symptoms. These include:
- Seeking medical supervision: It is crucial to have a healthcare professional monitor your condition during alcohol withdrawal, especially in severe cases.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as benzodiazepines, may be prescribed to help ease symptoms and prevent seizures.
- Proper nutrition and hydration: Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help the body recover during alcohol withdrawal.
- Therapy and support groups: Seeking therapy or joining support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of alcohol withdrawal.
Can You Prevent Alcohol Withdrawal?
While it is not always possible to prevent alcohol withdrawal, some steps can be taken to reduce the risk and severity of symptoms. Some ways to prevent or minimize alcohol withdrawal include:
- Seeking treatment for alcohol addiction before dependence develops
- Gradually reducing alcohol consumption instead of quitting abruptly
- Talking to a healthcare professional about safe detox methods
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with proper nutrition and exercise
- Seeking therapy or support groups to address underlying psychological issues related to alcohol use.
What Medications Are Used to Treat Alcohol Dependence?
Some of the commonly used medications to treat alcohol dependence include:
Disulfiram is an FDA-approved medication that has been used for treating alcohol dependence for over 60 years. It works by blocking the enzyme responsible for breaking down alcohol in the body, causing unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and headache when a person consumes alcohol while taking the medication. This creates a strong aversion to alcohol, making it easier for individuals to abstain from drinking.
Naltrexone is another FDA-approved medication that can help reduce cravings and compulsive drinking by blocking the effects of endorphins released during alcohol consumption. This medication can be taken in pill form (Revia) or as a monthly injection (Vivitrol).
Acamprosate is an FDA-approved medication that helps individuals abstain from alcohol by reducing the unpleasant symptoms of withdrawal, such as anxiety and insomnia. It works by balancing brain chemicals that are disrupted during heavy alcohol use.
While not specifically approved by the FDA for treating alcohol dependence, topiramate has shown promise in reducing drinking behaviors and preventing relapse. It works by reducing cravings and altering the pleasure response to alcohol.
Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam (Valium) and lorazepam (Ativan), are sometimes used in the short term to manage symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, such as anxiety and seizures. However, these medications can also be addictive and should be used under close supervision by a healthcare professional.
Treatment for Alcohol Withdrawal and Alcohol Addiction
Proper treatment for alcohol withdrawal is important, but it is only the first step in overcoming alcohol addiction. It is essential to seek ongoing support and therapy to address the underlying issues that may have led to excessive drinking.
Some options for treating alcohol addiction include:
- Inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation programs
- Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or family therapy
- Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous
- Medication-assisted treatment, which uses medication to manage cravings and withdrawals.
It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best course of treatment for each individual. With proper care and support, it is possible to overcome alcohol addiction and successfully manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
Seeking Help for Alcohol Withdrawal
If you or someone you know is experiencing alcohol withdrawal, it is important to seek medical help. Even if symptoms seem mild, it is better to err on the side of caution. Medical professionals can provide proper monitoring and treatment to ensure that complications do not arise.
Treatment for alcohol withdrawal may include medication to manage symptoms and prevent DTs, as well as therapy and support groups to address the underlying issues related to excessive drinking.
In addition to seeking medical help, it is also important to have a support system in place during and after alcohol withdrawal. This can include family, friends, or support groups who can offer encouragement and understanding during the recovery process.
Westwind Recovery® Can Assist with Alcohol Addiction
 Alcohol withdrawal can be a dangerous and potentially life-threatening process. It is crucial to seek proper medical help and support during this time. Remember, prevention is key, but if alcohol addiction has already developed, seeking treatment and ongoing support is the best way to overcome it.
Alcohol withdrawal can be a dangerous and potentially life-threatening process. It is crucial to seek proper medical help and support during this time. Remember, prevention is key, but if alcohol addiction has already developed, seeking treatment and ongoing support is the best way to overcome it.
If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol addiction and experiencing withdrawal symptoms, Westwind Recovery® in Los Angeles, California is here to help. Our experienced team provides compassionate care and evidence-based treatment for alcohol use disorders. So, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance with alcohol withdrawal and addiction. Recovery is possible, and we are here to support you every step of the way.

Dr. Deena is the Chief Clinical Officer of Westwind Recovery®, an award-winning outpatient treatment center in Los Angeles where she oversees the clinical and administrative program and treatment methods. Dr. Deena is a doctor of psychology and licensed clinical social worker since 1993. LCSW #20628. Originally from the East Coast, Dr. Deena has worked running treatment centers, worked as a therapist in psychiatric hospitals as well as school settings and currently has a thriving private practice in the LA area. Dr. Deena has appeared regularly on the Dr. Phil Show as an expert since 2003. She has also been featured on many other TV shows, podcasts and has contributed to written publications as well as podcasts.