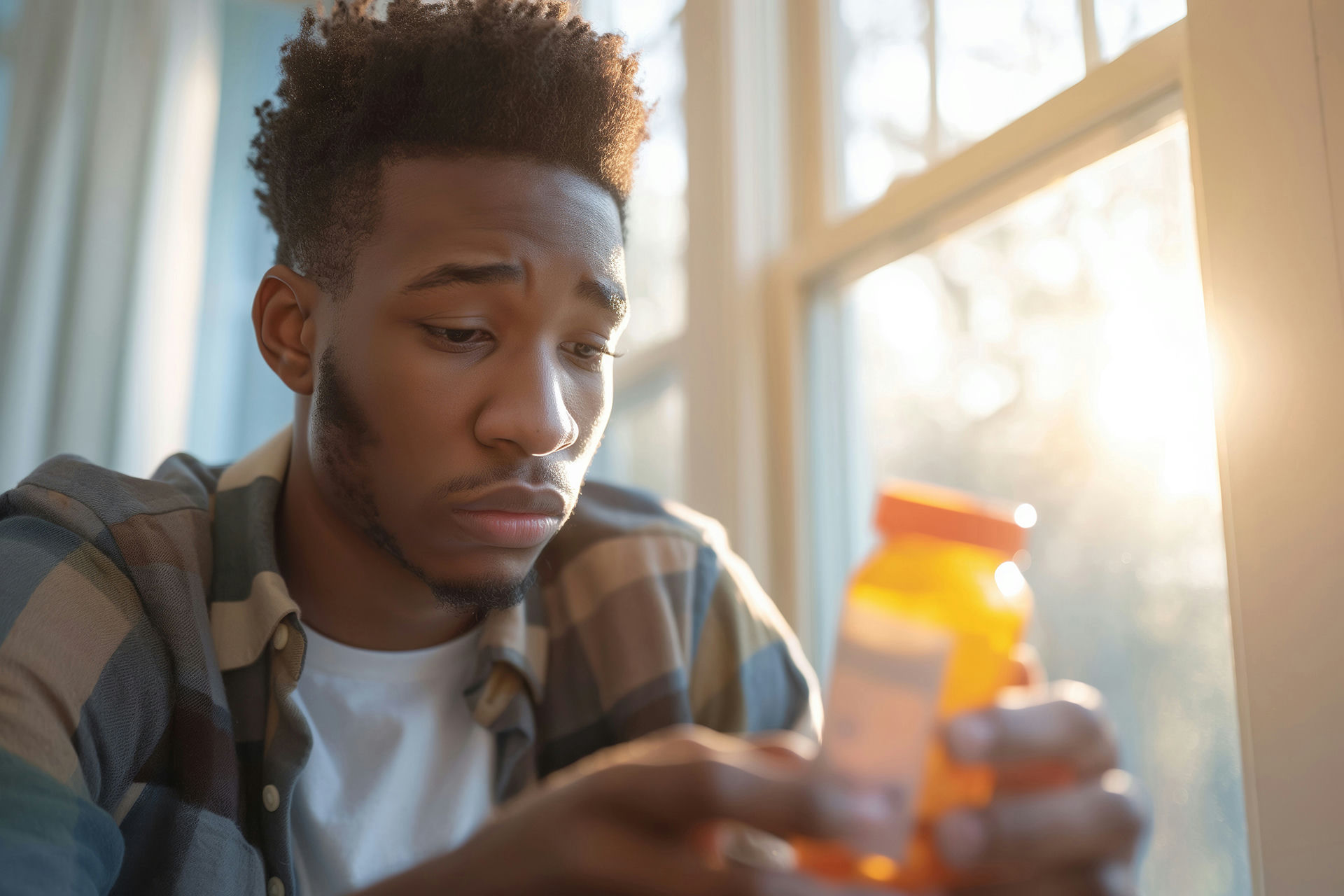
Recognizing ketamine dependency is so important because, while this medication can be helpful for pain and depression, it can also cause serious health issues when misused. Whether someone is using it recreationally or as a way to cope, ketamine abuse can sneak up quickly, impacting both mental and physical health. By noticing the early signs—like mood swings, pulling away from loved ones, or needing more to feel the same effect—you can take steps to get help before things get out of hand.
If you or someone close to you is struggling, you’re not alone, and help is available. Westwind Recovery® offers caring and personalized support to help you or your loved one move toward a healthier, happier, drug-free life. Their compassionate team is ready to help you every step of the way, offering tailored programs and counseling to rebuild a life full of hope and possibility.
What Are Ketamine Symptoms?
Ketamine affects the brain’s glutamate system, which plays a role in cognition, memory, and mood regulation. When used, ketamine can cause a variety of physical and psychological symptoms:
Short-Term Symptoms:
- Euphoria: Users may feel a temporary sense of happiness or emotional detachment.
- Hallucinations: Altered visual and auditory perceptions are common.
- Disconnection: A sensation of being detached from one’s body or surroundings, often referred to as the “K-hole.”
- Increased Heart Rate: Ketamine can cause tachycardia or a rapid heartbeat.
- Impaired Motor Skills: Users might appear clumsy, dizzy, or have slurred speech.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Ketamine can temporarily impair the ability to think clearly or focus.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some users may experience gastrointestinal distress shortly after taking the drug.
- Loss of Sensation: Ketamine can dull physical sensations, leading to a decreased sense of pain or touch.
Long-Term Symptoms of Ketamine Abuse:
- Cognitive Impairment: Chronic use can lead to memory loss, reduced attention span, and difficulty with decision-making.
- Urinary Tract Issues: Frequent use may cause bladder inflammation, urinary frequency, pain, or even permanent damage (ketamine bladder syndrome).
- Kidney and Liver Damage: Prolonged use can harm vital organs, leading to chronic health problems.
- Mental Health Issues: Users may develop depression, anxiety, or paranoia over time.
- Tolerance and Dependence: Repeated use often leads to requiring larger doses to achieve the same effect, increasing the risk of addiction.
- Psychosis and Hallucination Persistency: Long-term abuse may cause persistent hallucinations or delusions, even when not actively using the drug.
- Emotional Numbness: Users may feel emotionally detached or indifferent to their surroundings.
- Respiratory Issues: Prolonged use in high doses can lead to breathing problems or respiratory depression.
What Are the Warning Signs of Ketamine Dependency?
Ketamine dependency often develops slowly, making it hard to spot at first. Recognizing the warning signs early can make a big difference in helping someone get the support they need.
One key sign is compulsive use, where the person feels an uncontrollable need to use ketamine, even when it causes problems like strained relationships or work issues. Over time, they may develop tolerance, needing more of the drug to feel the same effects, which increases the risk of dependency.
You might also notice them neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home, or showing physical symptoms like fatigue, bladder problems, or weight loss. They may become more secretive or isolated, lying about their drug use or withdrawing from loved ones. Financial struggles are common as they prioritize spending on ketamine over essential needs.
Emotional instability is another sign to watch for, including mood swings, irritability, or signs of depression. If you see these behaviors in someone, it’s important to approach them with care and encourage seeking professional help. Early support can help them take the first steps toward recovery.
How Can You Spot Ketamine Addiction?
Spotting ketamine addiction early can make a significant difference in getting someone the help they need. Addiction often develops subtly, so being aware of key behavioral, physical, and psychological signs is crucial.
- Increased Usage: Needing higher doses to achieve the same effect or using more frequently.
- Obsessive Focus: Preoccupation with obtaining or using ketamine.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding family, friends, or responsibilities to use ketamine.
- Neglect of Responsibilities: Poor performance at work, school, or home due to ketamine use.
- Risky Behaviors: Engaging in dangerous activities under the influence of ketamine, such as driving.
- Slurred Speech: Difficulty articulating words or slow speech.
- Impaired Coordination: Clumsiness or difficulty with balance.
- Frequent Bladder Issues, chronic bladder pain, or increased urination, common with prolonged use.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Loss of appetite or weight.
- Dilated Pupils: Noticeable pupil enlargement even in normal lighting.
- Mood Swings: Alternating between euphoria and irritability or depression.
- Memory Issues: Difficulty recalling recent events or confusion.
- Hallucinations: Experiencing vivid visual or auditory distortions.
- Paranoia: Feeling excessively suspicious or fearful without cause.
- Detachment: A sense of being disconnected from reality or one’s body.
- Secrecy: Lying or being evasive about activities and whereabouts.
- Financial Problems: Spending excessive amounts of money to acquire ketamine.
- Loss of Interest: No longer caring about hobbies or activities once enjoyed.
- Strained Relationships: Increased conflicts or distance with loved ones.
- Isolation: Spending more time alone to use ketamine.
- Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness despite rest.
- Kidney Damage: Signs of urinary tract issues or kidney pain.
- Liver Problems: Jaundice or other symptoms of liver damage.
- Cognitive Decline: Difficulty concentrating or reduced mental clarity.
- Frequent Hospital Visits: Seeking help for overdoses or complications related to use.
If these signs are present, seeking professional help from addiction specialists or healthcare providers is crucial.
What Would Be the Intervention and Next Steps?
Helping someone with ketamine dependency requires compassion and a structured approach. Understanding their struggles, opening communication, and guiding them toward professional help are key steps.
Start by educating yourself about ketamine addiction, its effects, and the challenges of withdrawal. Research treatment options, including detox programs and support groups. Centers like Westwind Recovery® offer comprehensive recovery services tailored to individual needs. Being well-informed allows you to provide effective guidance.
Approach your loved one during a calm, private moment. Express concern using specific examples of their behavior, avoiding blame or judgment. Focus on sharing observations and support, using statements like, “I’m worried about you and want to help.” This fosters trust and encourages openness.
If a one-on-one conversation isn’t enough, organize a formal intervention with trusted friends, family, and a professional. Create a clear plan that outlines treatment options and emphasizes care and support. A well-structured intervention can motivate your loved one to take action.
Encourage them to consult a doctor, therapist, or addiction specialist who can recommend appropriate care. Explore detox programs and rehabilitation centers, like Westwind Recovery®, that provide the tools and support needed to address both physical and psychological aspects of addiction.
Recovery is an ongoing process that requires consistent support. Offer emotional and practical help, such as attending therapy sessions or simply being there during difficult moments. Encourage participation in aftercare programs like support groups or counseling to prevent relapse and maintain progress. Your continued support can make a lasting impact on their recovery journey.
What Are the Physical Withdrawal Symptoms of Ketamine Addiction?
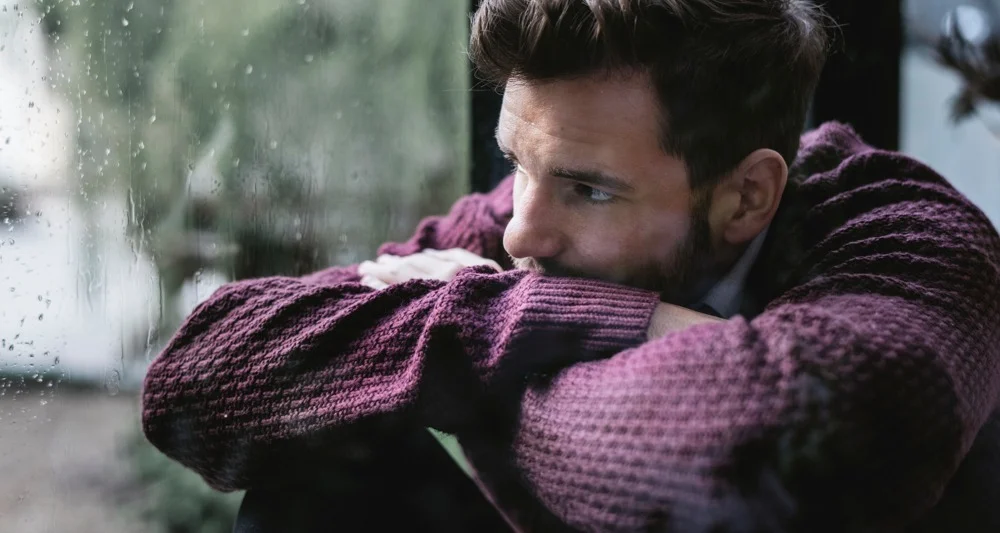 When ketamine use is reduced or stopped, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms. These can range from mild to severe depending on the level of dependence. The top 15 most common physical withdrawal symptoms include:
When ketamine use is reduced or stopped, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms. These can range from mild to severe depending on the level of dependence. The top 15 most common physical withdrawal symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating, even without physical activity.
- Tremors: Shaking hands or body tremors.
- Muscle Pain: Generalized aches or cramps, particularly in the limbs.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive discomfort, often accompanied by a lack of appetite.
- Increased Heart Rate: Rapid heartbeat or palpitations.
- Headaches: Intense or persistent headaches.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or unsteady on your feet.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary visual disturbances.
- Respiratory Issues: Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Urinary Problems: Difficulty urinating or increased bladder discomfort, a common side effect of ketamine abuse.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced interest in food, often leading to weight loss.
- Seizures: In severe cases, withdrawal can trigger seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of high-dose or long-term use.
- Body Temperature Fluctuations: Experiencing hot flashes or chills without an apparent cause.
These symptoms can be distressing and challenging to manage without professional support. A medically supervised detoxification program is often recommended to ensure safety and comfort during the withdrawal process.
Westwind Recovery® Can Assist With Ketamine Addiction in LA
Westwind Recovery® offers comprehensive programs designed to help individuals overcome ketamine dependency. Our holistic approach includes:
- Therapeutic Support: Individual therapy and group therapy to address the underlying causes of addiction.
- Aftercare Services: Continuous support to maintain long-term sobriety.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Tailored interventions based on the individual’s needs.
- Sober Living Homes: Providing a safe, structured, and supportive environment for individuals transitioning from treatment to independent living, promoting accountability and fostering community.
- Chronic Pain Management: Long-term care and relapse prevention for sustained recovery.
Take the first step toward a healthier, drug-free life—contact us today to start your journey to recovery.

Dr. Deena is the Chief Clinical Officer of Westwind Recovery®, an award-winning outpatient treatment center in Los Angeles where she oversees the clinical and administrative program and treatment methods. Dr. Deena is a doctor of psychology and licensed clinical social worker since 1993. LCSW #20628. Originally from the East Coast, Dr. Deena has worked running treatment centers, worked as a therapist in psychiatric hospitals as well as school settings and currently has a thriving private practice in the LA area. Dr. Deena has appeared regularly on the Dr. Phil Show as an expert since 2003. She has also been featured on many other TV shows, podcasts and has contributed to written publications as well as podcasts.